|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||

UNIT
1 : ALGEBRA PREP
LESSON
1: REAL NUMBERS & RADICALS

Note: In these notes, we are talking about real numbers unless otherwise stated.
Intervals:
![]()
The interval can also be illustrated on a number line as below.

OR
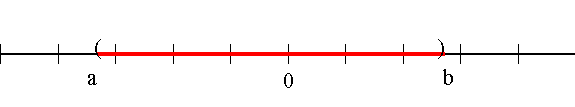
NOTE: Open circles or round brackets indicate that the end point indicated is not included.
![]()
The interval can also be illustrated on a number line as below.

OR

NOTE: Closed circles or square brackets indicate that the end point indicated is included.


![]()
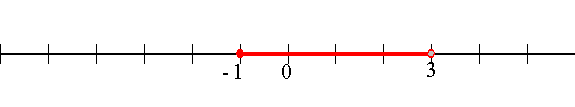
![]()
![]()
![]()

![]()
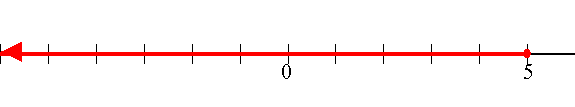
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()

![]()

![]()
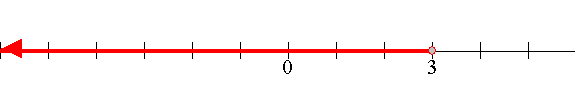
REAL NUMBERS
- RADICALS
Examples Of Radicals:

NOTE: Each of these examples is an irrational
real number.
Properties of Radicals:
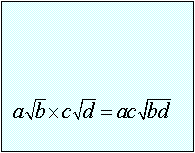
Example 1:
![]()
Mixed
and Entire Radicals:

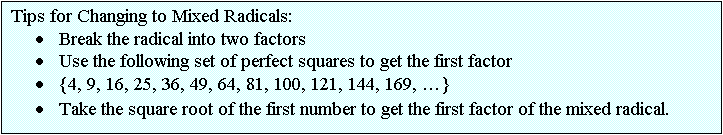

Multiplying
Radicals:

Addition
and Subtraction of Radicals:

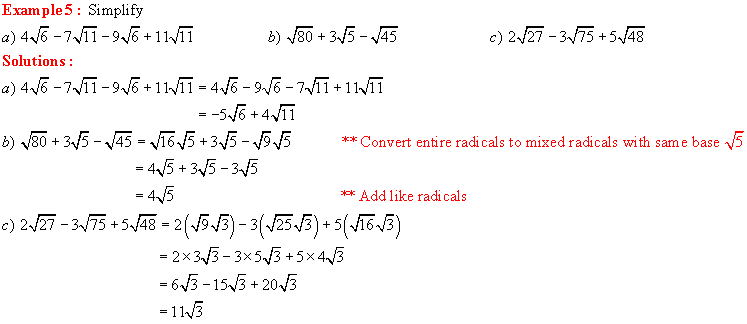
![]()
Solutions:
Again we
follow the rules of ordinary algebra for expanding
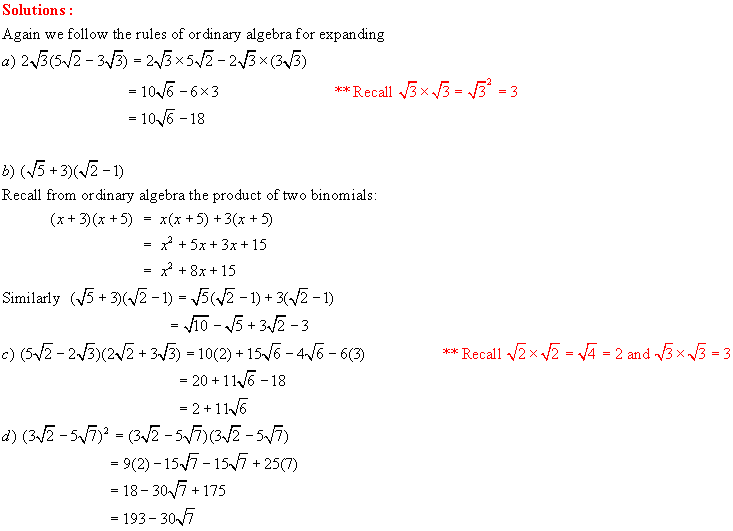
Division
of Radicals:
Recall
all of the properties of radicals mentioned above:

Division
of Radicals with Irrational denominators: