|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||

UNIT
2 : FUNCTIONS & TRANSFORMATIONS
LESSON 5:
INVERSES OF FUNCTIONS HOMEWORK QUESTIONS
1. For each function given, determine the ordered
pairs of the inverse and whether the inverse is a function or not.
(a) f = {(-2, -5), (-1, -3), (0, -1), (1, 1), (2, 3)}
(b) g = {(2, 0), (6, 3), (6, -3), (10, 4), (10, -4)}
(c) h = {(-2, 5), (-1, 3), (0, 1), (1, 3), (2, 5)}
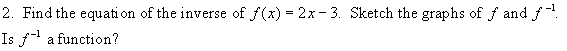
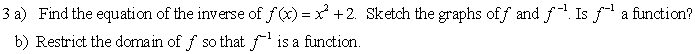
4. For each relation given, determine the
ordered pairs of the inverse and draw its graph. State the domain and range of
the inverse in each case.
a)
b)
5. (i)
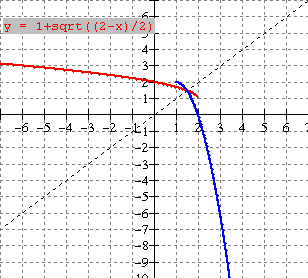
The graph of the relation y = f(x) [blue] and its inverse y = f 1
(x) [red] are shown below. Evaluate each of the following
a) f(-2) b) f 1 (3) c) f
1 (2) d) f(-5)
(ii) Is f 1 a function ?? Explain
6. Given the function g(x) = 3x 1, find an
equation for g-1 (x) and evaluate each of the following:
a) g(-1) b) g 1 (2) c) g
1 (-3) d) g(-5) e)
½ (g 1 (-2) 1)
f) g(a) g) g 1 (a + 2) h) g 1 (a + 1) - g 1 (a)
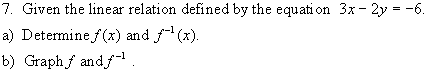
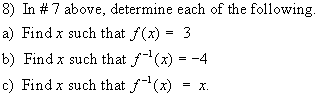
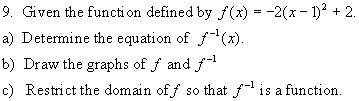
1. For each function given, determine the ordered
pairs of the inverse and whether the inverse is a function or not.
(a) f = {(-2, -5), (-1, -3), (0, -1), (1, 1), (2, 3)}
Solution: f- -1 = {(-5, -2), (-3, -1), (-1, 0), (1, 1), (3, 2)} ** Interchange x and y components of the ordered pairs
Yes , f 1 is a function as no two ordered pairs have the same first element.
(b) g = {(2, 0), (6, 3), (6, -3), (10, 4), (10, -4)}
Solution: g 1 = {(0, 2), (3, 6), (-3, 6),
(4, 10), (-4, 10)} ** Interchange x and y components of the ordered pairs
Yes , g 1 is a function as no two ordered pairs have the same first element.
(c) h = {(-2, 5), (-1, 3), (0, 1), (1, 3), (2, 5)}
Solution: h 1 = {(5, -2), (3, -1), (1, 0),
(3, 1), (5, 2)} ** Interchange x and
y components of the ordered pairs
No! , h 1 is a not function as some ordered pairs have the same first element eg. -- (5, 2) and (5, -2).
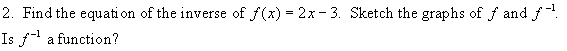 .
.
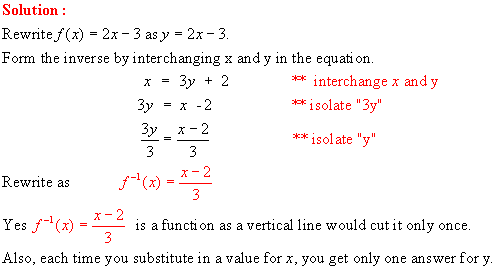
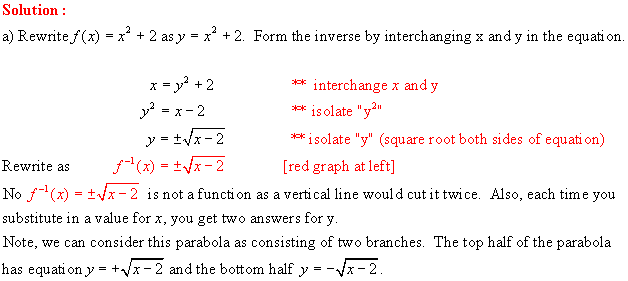
4. For each relation given, determine the
ordered pairs of the inverse and draw its graph. State the domain and range of
the inverse in each case.
a)
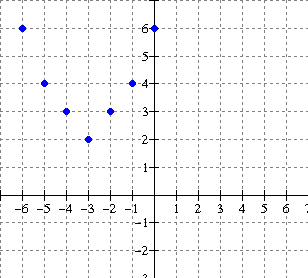
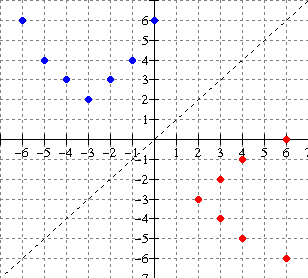
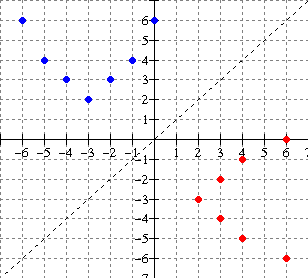
Solution:
From the graph, the ordered pairs are {(-6,6), (-5, 4), (-4, 3), (-3,
2), (-2, 3),
(-1, 4), (0, 6)}
The
ordered pairs of the inverse are:
{(6,-6), (4, -5), (3, -4), (2, -3), (3, -2),
(4, -1), (6, 0)} **
interchange x and y
Note the reflection in the line
y = x (dashed)
Domain of inverse: {2, 3, 4, 6} -- set of all x components of the ordered pairs of f 1.
Range of inverse: {-6, -5 , -4, -3, -2, -1, 0} -- set of all y components of the ordered pairs of f 1.
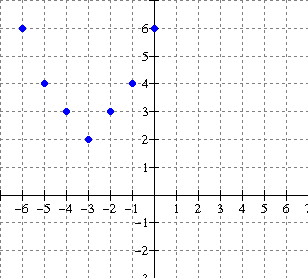
b)
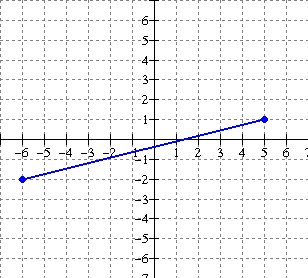
 Solution: From the graph, the ordered
pairs of the end points are (-6,-2) and (5, 1).
Solution: From the graph, the ordered
pairs of the end points are (-6,-2) and (5, 1).
The ordered pairs of the end points of the inverse [red graph] are:
(-2, -6) and (1, 5) ** interchange x and y
Note the reflection in the
line y = x (dashed)
Domain of inverse: The lowest value of x is at the left endpoint (-2, -6), namely x = -2.
The highest value of x is at the right end point (1, 5), namely x = 1. Therefore the domain is:
![]()
Range of inverse: The lowest value of y is at the endpoint (-2, -6), namely y = -6.
The highest value of y is at the top end point (1, 5), namely y = 5. Therefore the range is:
![]()
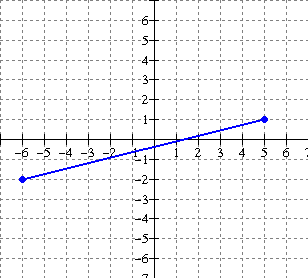
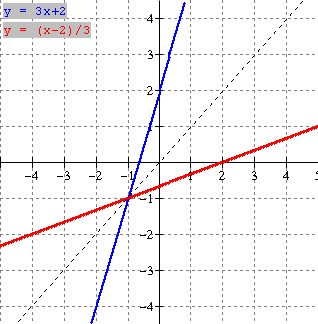
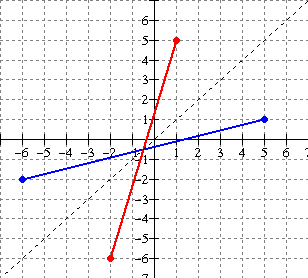
5. (i)
The graph of the relation y = f(x) [blue] and its inverse y = f 1
(x) [red] are shown below. Evaluate each of the following
a) f(-2) b) f 1 (3) c) f
1 (2) d) f(-5)
(ii) Is f 1 a function ?? Explain
Solution:
(i)
a) For f(-2), we want the value of y on the
blue graph when x = -2. Therefore
f(-2) = 3.
b) For f 1 (3), we want the value
of y on the red graph when x = 3.
Therefore f 1 (3) =
-2.
c) f 1 (2) = -3
d) f(-5) = 4
(ii) No f 1 is not a function as a
vertical line would cut it twice if drawn where x = 2 of x = 3 or x = 6.
6. Given the function g(x) = 3x 1, find an
equation for g-1 (x) and evaluate each of the following:
a) g(-1) b) g 1 (2) c) g
1 (-3) d) g(-5) e)
½ (g 1 (-2) 1)
f) g(a) g) g 1 (a + 2) h) g 1 (a + 1) - g 1 (a)
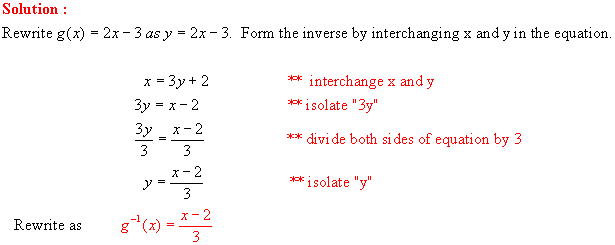
a) g (-1) = 2(-1) - 3 = -5 b)
g 1 (2) = (2 2)/3 = 0 c) g 1 (-3) = (-3 2)/3 = -5/3 d)
g(-5) = 2(-5) 3 = -13
e) ½ (g 1 (-2) 1) = ½ [(-2 2)/3
1] = ½ [-4/3 3/3] = ½ (-7/3) = -7/6 f) g(a) = 2(a)-3 = 2a 3 g)
g 1(a+2) = [(a+2)-2]/3 = a/3
h) g 1 (a + 1) - g 1
(a) = [(a+1)-2]/3 [(a) 2]/3 = (a-1)/3
- (a-2)/3
![]()
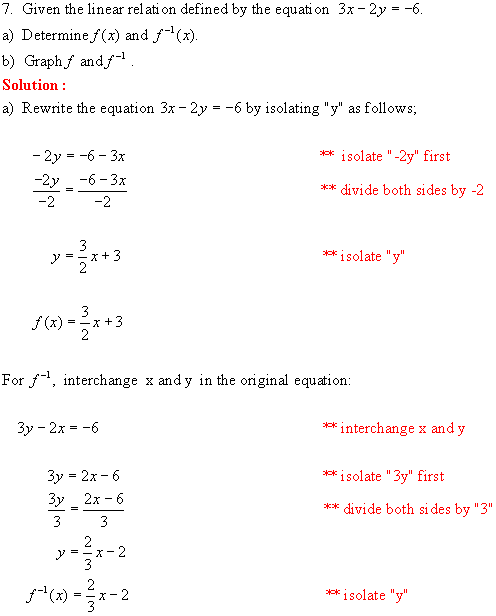
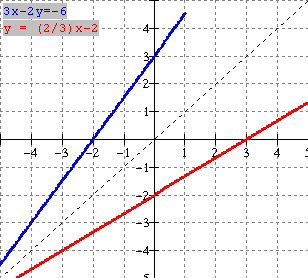
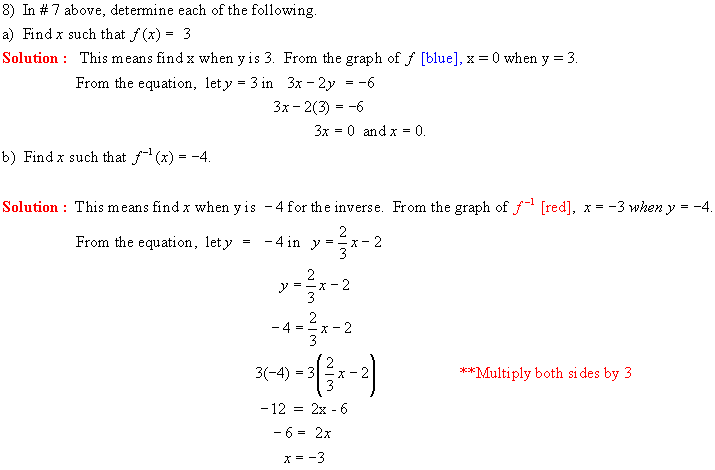
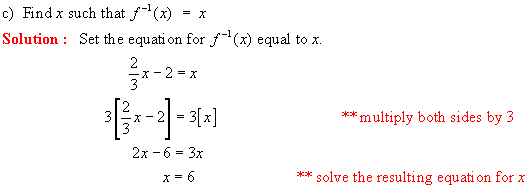
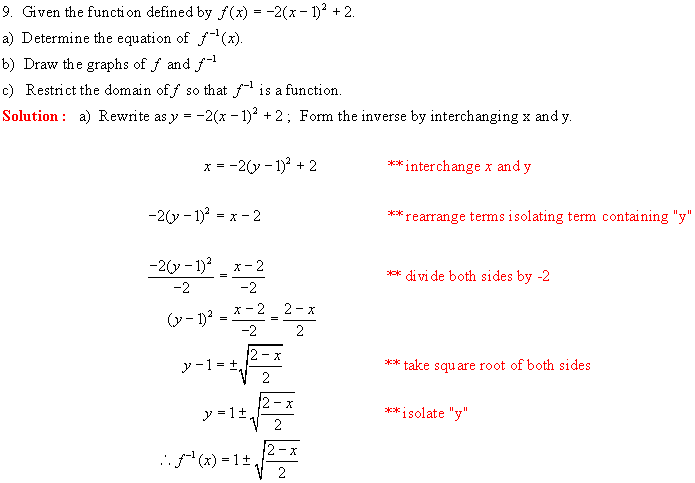
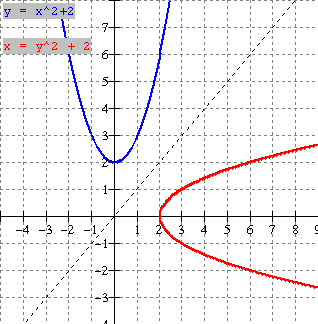
b) Using y = x2 as our base curve,
we first graph f (x) = -2(x 1)2 + 2 using transformations. [see
lesson 8]
·
Reflection
in the x-axis
·
Vertical
stretch factor 2
·
Horizontal
translation right 1 unit
·
Vertical
translation up 2 units
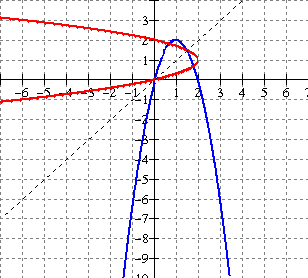
The
mapping form is (x, y)
------------------------ΰ (x + 1, -2y + 2) . Use key points from y = x2 graph to obtain image points
(-2, 4)
----------------------ΰ (-1, -6)
(-1, 1)
----------------------ΰ (0, 0)
(0, 0) -----------------------ΰ (1, 2)
Vertex
(1,1)
------------------------ΰ (2, 0)
(2, 4)
-----------------------ΰ (3. 6) [blue graph at left]
The inverse
is obtained by interchanging x and y coordinates above. [red graph at
left]