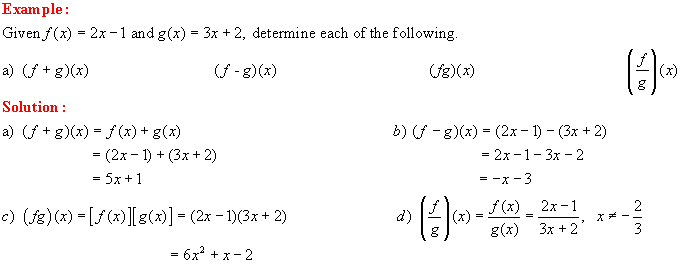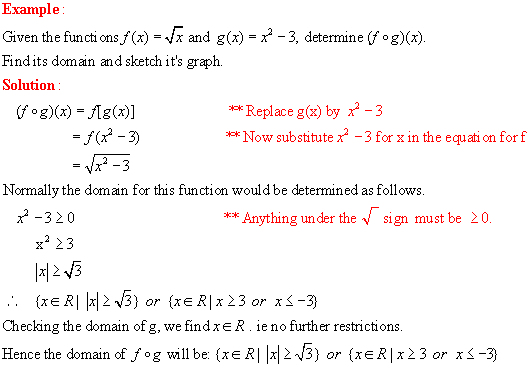|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||
UNIT
2 : FUNCTIONS
LESSON
9: FUNCTIONS REVIEW & SUMMARY
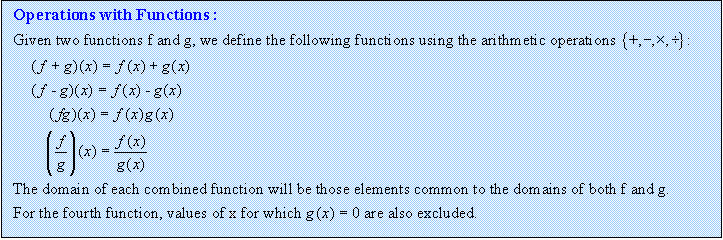
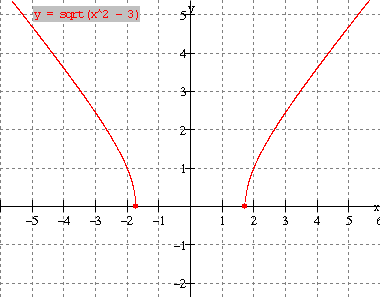
1. Functions: definition, notation, tests, domain and range - see lesson 1.
Defn: A function is a relation such that for each value of x, there
corresponds exactly one value of y.
Tests:
·
Vertical
line test if a vertical line cuts the graph more than once -- not a function
·
If no two ordered pairs have the same first element, then the relation is a function
·
Substitute
in a value for x; if you get more than one answer for y not
a function
Tips for finding domain:
·
Set
of all first components of the ordered pairs.
·
Is
there a largest value for x? Is there a
smallest value for x?
·
Are
there any restrictions on x?
Tips for finding range:
·
Set
of all second components of the ordered pairs.
·
Is
there a largest value for y? Is there a
smallest value for y?

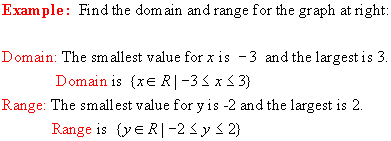
![]()
2. Transformations:
![Text Box: In summary, to graph y = af [k(x m)] + n from the graph of y = f(x), follow these ideas:
· If a < 0, we have a reflection in the x-axis
· If k < 0, we have a reflection in the y-axis
· If 1 < a < 1, we have a vertical compression
· If a > 1 or a < - 1, we have a vertical stretch
· If 1 < k < 1, we have a horizontal stretch, factor 1/k
· If k > 1 or k < - 1, we have a horizontal compression, factor 1/k
· The value of m gives the horizontal translation (shift)
· The value of n gives the vertical translation (shift)](./review_files/image010.gif)
Example:
Describe -2f [½ (x 3)]
1 relative a given function y = f(x)
·
Reflection
in the x-axis
·
Vertical
stretch factor 2
·
Horizontal
stretch factor 2
·
Horizontal
translation right 3
·
Vertical
translation(shift) down 1
To
graph, take points on original graph of y = f(x) and use the mapping form to
determine image points -- see Lesson 7.

3. Inverses:
![]()
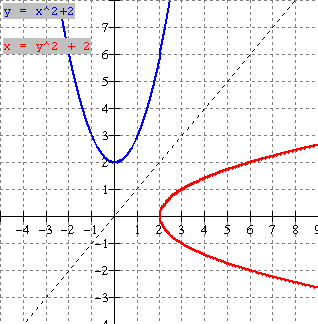


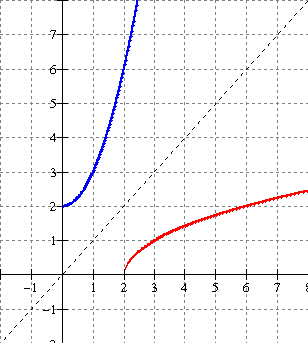

In summary, if we restrict
the domain of the given parabola to that half either to the right or left
of the vertex, the inverse will be a function.
![]()