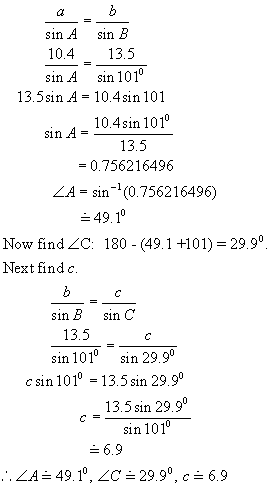|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|||||||||||

UNIT 6 : BASIC
TRIGONOMETRY WITH TRIANGLES
LESSON
3: SINE LAW
The
Sine Law:
The sine
law is used to solve oblique triangles, that is triangles which are not right angled.
A

![]() c b
c b
![]() B a C
B a C
Given
two angles and a side (AAS case)
Example 1:
![]()

 A
A
c b
![]() B 48o 29o C
B 48o 29o C
22.4 cm
Solution:
First
find the measure of < A: 180o – (48o + 29o)
= 103o
Now find
c using the sine law:
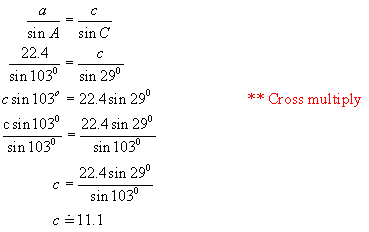
Now find
b using the sine law:
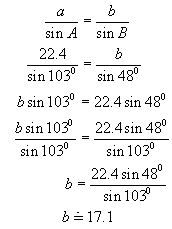
Given
two sides and an ACUTE angle (< 900) opposite one of the sides
[the non-contained angle] (SSA)
Example 2:
![]()
Note:
Here the longer side (23.1) is opposite the given acute angle < E is
acute. There is only one triangle in this case.
 D
D
16.4 cm 23.1 cm
![]() E 56.4o F
E 56.4o F
Solution:
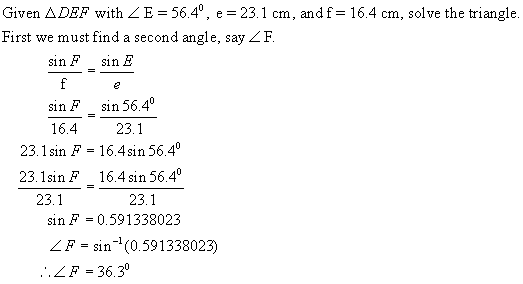
Now find
< D: 180 – (56.40 + 36.30)
= 87.30
Next
find d using the sin law:
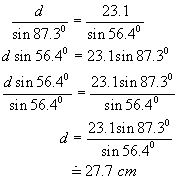
Given
two sides and an ACUTE angle where the shorter side (b) is opposite the given angle
(<
B) (SSA)
Example 3:
Solution: There are 3
possibilities here,
one of which is the so-called ambiguous case where there are two triangles
which satisfy the given conditions.
 C
C
b a
![]() A ( B
A ( B

![]()
 C
C
b h a
![]()
![]() A ( B
A ( B
D
![]()

![]()
 C
C
b h b
a
![]()
![]() A1 ( B
A1 ( B
D A2
![]()
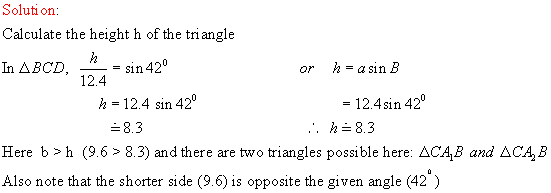

![]()
 C
C
9.6 h 9.6
12.4
![]()
![]() A1 420 B
A1 420 B
A2
Hence there are two triangles to
solve here.
Triangle 1:
 C
C
9.6 12.4
![]() A1 420 B
A1 420 B
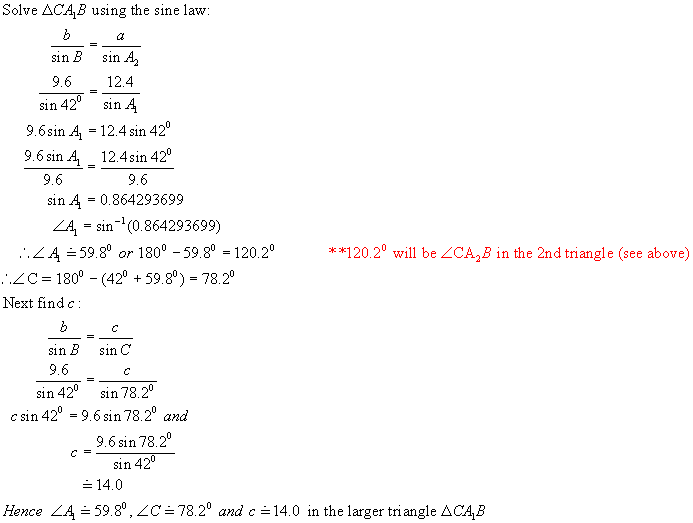
Triangle 2 : Recall from above that < CA2B = 120.20

 C
C
9.6 12.4
![]() A2 120.20 420
B
A2 120.20 420
B
![]()
C
b=h a
![]()
![]() A B
A B
![]()

![]()
 C
C
b h b
a
A A
![]()
![]() ( B
( B
The
SSA case where the given angle B is OBTUSE (> 900)
Example 4:
![]()
 C
C
b a
![]() A B
A B
![]()
 C
C
b a
![]() A B
A B
Example 4(a):
![]()
 C
C
13.5 10.4
![]()
![]() A B
A B
1010
Solution: This is the SSA case
with a given obtuse angle and the side opposite this angle is the
longer side.
There will
be only one triangle to solve.
First
find < A using the sine law.