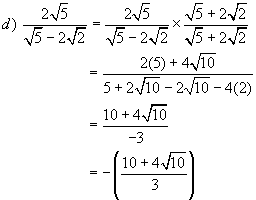|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||

UNIT 3 : QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS & EQUATIONS
LESSON
5: RADICALS
Examples Of Radicals:

Properties of Radicals:
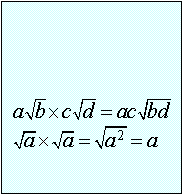
Example 1:
![]()
Mixed
and Entire Radicals:
Example 2:
Write as mixed radicals.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Solutions:
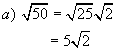
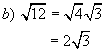
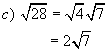
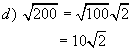
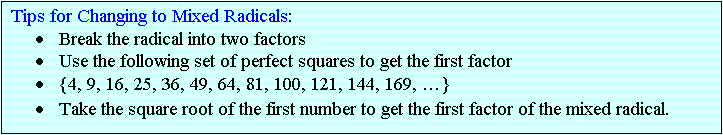
Example 3:
Write as entire radicals.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Solutions:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Multiplying
Radicals:
Example 4:
Simplify
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Solutions:
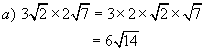
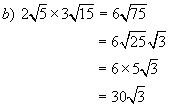
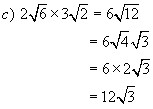
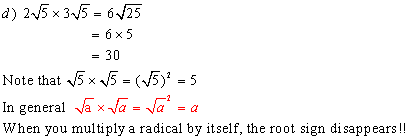
Addition
and Subtraction of Radicals:
Radicals are added/subtracted just as in ordinary algebra
using LIKE TERMS.
Examples:
2x – 3y + 5x –
6y = 2x + 5x – 3y – 6y = 7x – 9y
Similarly ![]()
Example 5:
Simplify
![]()
![]()
![]()
Solutions:
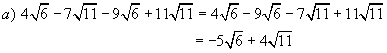
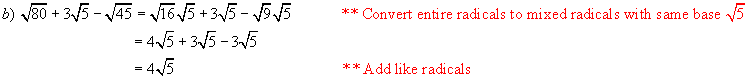
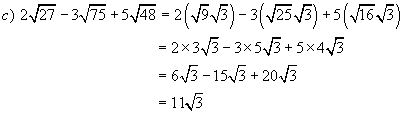
Example 6:
Simplify
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Solutions:
Again we
follow the rules of ordinary algebra for expanding
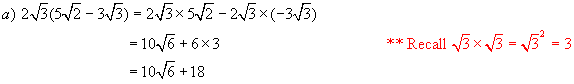
![]()
Recall
from ordinary algebra the product of two binomials:
(x + 3)(x + 5) = x(x + 5) + 3(x + 5)
= x2
+ 5x + 3x + 15
= x2
+ 8x + 15
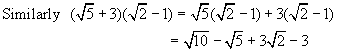
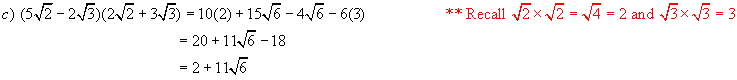
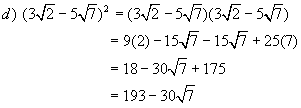
Division
of Radicals:
Recall
all of the properties of radicals mentioned above:
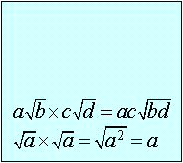
Example 7:
Simplify
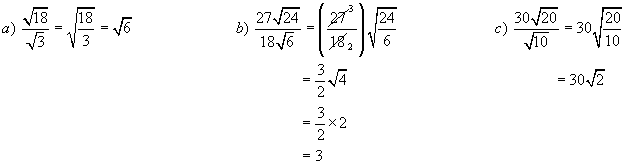
Division
of Radicals with Irrational denominators: Examples: ![]()
These are simplified by a
process called rationalizing the denominator.
Example 8:
Simplify by rationalizing the
denominator.
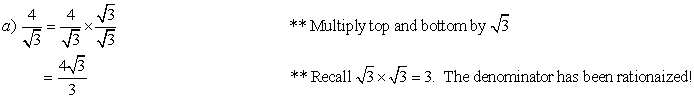
Example 9:
Simplify
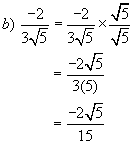
Example 10: Simplify

Example 11: Simplify